-
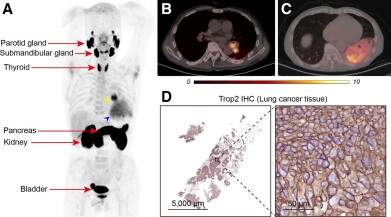 [18F]AlF-RESCA-T4 immuno-PET/CT imaging of patient with primary lung cancer. (A–C) Maximum-intensity projection (A) and fusion images (B and C) of [18F]AlF-RESCA-T4 immuno-PET/CT. Yellow arrowhead indicates presence of left hilar occupancy and lymph node in fusion image. Blue arrowhead indicates presence of distal lung atelectasis. Physiologic uptake of [18F]AlF-RESCA-T4 by normal organs and tissues is indicated by red arrows. (D) Histologic examination of resected left hilar mass showed intense Trop2 staining. IHC = immunohistochemistry. Credit: Image created by W. Wei, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
[18F]AlF-RESCA-T4 immuno-PET/CT imaging of patient with primary lung cancer. (A–C) Maximum-intensity projection (A) and fusion images (B and C) of [18F]AlF-RESCA-T4 immuno-PET/CT. Yellow arrowhead indicates presence of left hilar occupancy and lymph node in fusion image. Blue arrowhead indicates presence of distal lung atelectasis. Physiologic uptake of [18F]AlF-RESCA-T4 by normal organs and tissues is indicated by red arrows. (D) Histologic examination of resected left hilar mass showed intense Trop2 staining. IHC = immunohistochemistry. Credit: Image created by W. Wei, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
News
Novel radiotracer identifies critical cancer biomarker, opens door to new therapeutic target for solid tumours
Dec 24 2024
A new molecular imaging agent has been found to accurately identify a crucial biomarker which is found in different types of cancer. Precise visualisation of the trophoblast cell surface antigen 2 (Trop2) biomarker will provide physicians with valuable diagnostic insights, allow for the development of personalised treatment plans, and objective assessment of tumour treatment responses, write researchers in the Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Trop2 has recently become of greater interest to oncology researchers because of the role it plays in cell-renewal, proliferation, transformation and organ development. It is commonly found in triple-negative breast cancer, colorectal cancer, gastric carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, and non–small cell lung cancer, among other solid tumors.
“Trop2 is an emerging biomarker for developing next-generation diagnostic and therapeutic agents for solid tumours and has the potential to be a game-changer for cancer treatment,” said Dr. Weijun Wei, associate research professor in the department of nuclear medicine at Renji Hospital School of Medicine at Shanghai Jiao Tong University in China.
“However, efficiently visualising Trop2 expression and selecting patients who might benefit from Trop2-targeted therapies is a clinical challenge.”
Wei and colleagues have developed two novel Trop2-targeted radiotracers:
- 18F-AlF-RESCA-T4,
- 18F-AlF-RESCA-RT4,
to further the research into the Trop2 biomarker.
Preclinical imaging and blocking studies were performed on tumour-bearing mice to determine safety and efficacy. A pilot clinical trial including three patients with suspected lung cancer was also conducted. This trial included a head-to-head comparison of PET/CT imaging with 18F-AlF-RESCA-T4, 18F-AlF-RESCA-RT4, and a previously developed radiotracer, 68Ga-NOTA-T4.
Prominent tumour uptake was observed with both 18F-AlF-RESCA-T4 and 18F-AlF-RESCA-RT4, however the latter showed substantially reduced kidney accumulation. In the clinical trial’s head-to-head comparison, 18F-AlF-RESCA-T4 performed best. Initial 18F-AlF-RESCA-T4 immuno-PET/CT imaging demonstrated the ability to visualise Trop2 expression in suspected lung cancer patients; it was also able to differentiate lung inflammation, such as tuberculosis, from cancer.
“PET imaging with 18F-AlF-RESCA-T4 will allow physicians to identify patients with Trop2-positive tumours so they can receive Trop2-targeted treatments,” noted Wei.
The authors of “Immuno-PET/CT Imaging of Trop2 with [18F]AlF-RESCA-T4 Differentiates Lung Cancer from Inflammation” include Wei Huang, You Zhang, Shuxian An, Xinbing Pan, Xinyuam Zhou, Hongda Shao, Gang Huaung, Jianjun Liu, and Weijun Wei, Department of Nuclear Medicine, Institute of Clinical Nuclear Medicine, School of Medicine, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China; Min Cao, Department of Thoracic Surgery, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China; Yanfei Wu, Yihui Guan, and Fang Xie, Department of Nuclear Medicine and PET Center, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China; and Fabrizia Gelardi and Arturo Chiti, Università Vita-Salute San Raffaele, Milan, Italy, and Nuclear Medicine Department, IRCCS San Raffaele, Milano, Italy.
To read more visit: 10.2967/jnumed.124.268751
-- EurekAlert.org
Digital Edition
Lab Asia Dec 2025
December 2025
Chromatography Articles- Cutting-edge sample preparation tools help laboratories to stay ahead of the curveMass Spectrometry & Spectroscopy Articles- Unlocking the complexity of metabolomics: Pushi...
View all digital editions
Events
Jan 21 2026 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 28 2026 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 29 2026 New Delhi, India
Feb 07 2026 Boston, MA, USA
Asia Pharma Expo/Asia Lab Expo
Feb 12 2026 Dhaka, Bangladesh


















