-
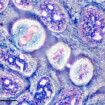
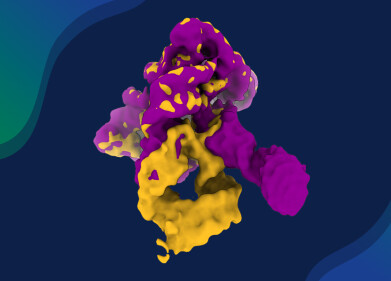
 Using an X-ray diffractor to study the sigma bond. Credit: Yusuke Ishigaki
Using an X-ray diffractor to study the sigma bond. Credit: Yusuke Ishigaki
Research news
Scientists discover single-electron bond in crystal structure of carbon compound
Feb 14 2025
Discovery of stable single-electron covalent bond in carbon compound validates a century-old theory
Covalent bonds, in which two atoms are bound together by sharing a pair of electrons, form the scaffolding that underpins the majority of organic compounds. In 1931, the Nobel Laureate Linus Pauling suggested that covalent bonds made from just a single, unpaired electron could exist but these single-electron bonds would likely be much weaker than a standard covalent bond involving a pair of electrons.
Since then, single-electron bonds have been observed, but never in carbon or hydrogen – the hunt for one-electron bonds shared between carbon atoms had so far eluded scientists.
Now, a team of researchers from Hokkaido University has isolated a compound in which a single electron is shared between two carbon atoms in a remarkably stable covalent bond, known as a sigma bond.
“[Explaining] the nature of single-electron sigma-bonds between two carbon atoms is essential to gain a deeper understanding of chemical-bonding theories and would provide insights into chemical reactions,” explained Professor Yusuke Ishigaki, Department of Chemistry, Hokkaido University, a co-author of the study.
Breakthrough and controversy: the scientific and ethical legacy of Henrietta Lacks and her immortal HeLa cells
Regarded from the perspective of expanding the knowledge base, there can be little doubt that the discovery and exploitation of the HeLa cell line is one of the most consequential stories in the hi... Read More
The single-electron bond was formed by subjecting a derivative of hexaphenylethane, which contained an extremely stretched out paired-electron covalent bond between two carbon atoms, to an oxidation reaction in the presence of iodine. The reaction produced dark violet-coloured crystals of an iodine salt.
The team used X-ray diffraction analysis to study the crystals and found that the carbon atoms in them were extremely close together, suggesting the presence of single-electron covalent bonds between carbon atoms. They were then able to confirm this using Raman spectroscopy.
“These results thus constitute the first piece of experimental evidence for a carbon-carbon single-electron covalent bond, which can be expected to pave the way for further developments [in this branch] of chemistry for this scarcely explored type of bonding,” said Takuya Shimajiri, the lead author of the paper and now at the University of Tokyo.
For further reading please visit: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39322667/
Digital Edition
Lab Asia Dec 2025
December 2025
Chromatography Articles- Cutting-edge sample preparation tools help laboratories to stay ahead of the curveMass Spectrometry & Spectroscopy Articles- Unlocking the complexity of metabolomics: Pushi...
View all digital editions
Events
Jan 21 2026 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 28 2026 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 29 2026 New Delhi, India
Feb 07 2026 Boston, MA, USA
Asia Pharma Expo/Asia Lab Expo
Feb 12 2026 Dhaka, Bangladesh