Laboratory products
Leveraging AI in Freeze-Drying Process Development: A Starting Point, Not the Finish Line
Nov 05 2025
Artificial intelligence tools such as ChatGPT, Gemini, and DeepSeek are increasingly being explored as aids in pharmaceutical and biotech freeze-drying (lyophilisation) process development. From drafting protocols and suggesting equipment or excipients, AI offers a rapid first step in early-stage design. Yet, while AI can accelerate ideation, expert judgement remains indispensable for robust, scalable, and regulatory-compliant processes.
Product-Specific Requirements
Every lyophilised product has distinct physicochemical characteristics requiring a tailored approach. Effective cycle design depends on detailed analytical data, including:
- Freeze-Drying Microscopy (FDM) and Modulated Differential Scanning Calorimetry (mDSC) to determine collapse temperature, eutectic point, and glass transition.
- Empirical evaluation of key quality attributes such as cake structure, residual moisture, and reconstitution time.
At present, AI cannot predict how novel products will behave under freeze-drying conditions. Such understanding demands laboratory data and expert interpretation.
Formulation Development: Beyond AI’s Current Reach
While AI can generate preliminary formulation suggestions, it lacks capacity to assess complex molecular behaviour or excipient interactions. Formulation work depends on understanding sample stability, degradation pathways, and specific excipient functionality—variables that cannot be reliably generalised by large-language models.
Moreover, AI outputs may draw from inconsistent or non-validated data sources, leading to inaccuracies when used to guide formulation design. Expert oversight and experimental verification remain essential to ensure stability, efficacy, and safety.
Equipment and Scale Considerations
AI tools also cannot account for performance variability between laboratory, pilot, and GMP-scale freeze-dryers. Factors such as heat transfer efficiency, condenser capacity, and chamber pressure control significantly influence cycle success and must be empirically calibrated for each system.
Regulatory and Quality Integration
While AI summarises guidelines, it lacks awareness of evolving regulatory expectations and inspection trends. CDMOs like Biopharma Group integrate these requirements from the outset, ensuring:
- Alignment with ISO 9001, ISO 13485, and QbD principles.
- Analytical validation plans that meet specific regional regulatory needs.
- Seamless technology transfer between R&D and production environments.
Case Study: Comparing AI Simulation vs Expert Design
To assess AI’s practical utility, Biopharma Group compared a ChatGPT-generated freeze-drying cycle with one designed by its R&D team for a 10% Dextran 40K solution.
Prompt entered into ChatGPT: “Simulate a freeze-drying cycle trace for a 10% Dextran solution in a DIN10R vial with a 2 mL fill and present as a graph.”
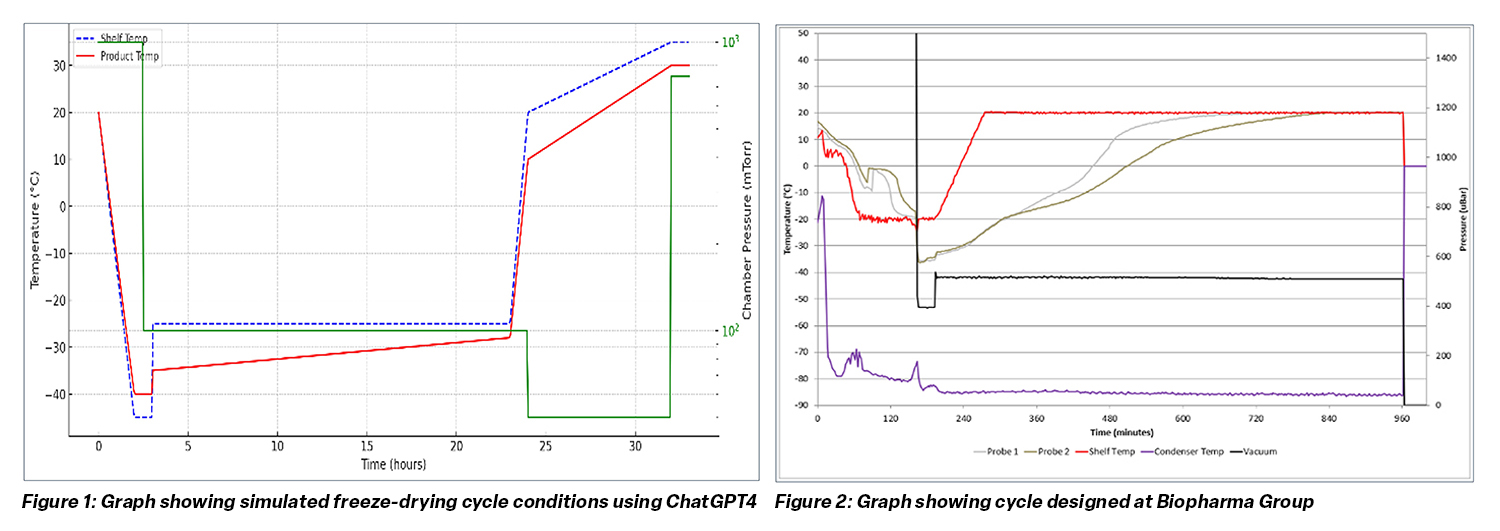
Key findings:
- The AI-generated cycle suggested viable shelf temperatures and chamber pressures but produced unreliable predictions for product temperature profiles and drying duration.
- The Biopharma Group designed cycle achieved high-quality cakes in approximately half the total process time.
- These results confirm that while AI can assist with early-stage design, human expertise is critical for developing reproducible and efficient processes.
Conclusion
AI emerges as a useful co-pilot in lyophilisation process development, accelerating preliminary work, collating reference data, and generating conceptual models. However, for formulation optimisation, equipment calibration, and regulatory alignment, experienced scientists and validated experimentation remain the cornerstones of success. AI is best viewed not as a replacement for human expertise, but as a powerful starting point that enhances it.
Digital Edition
Lab Asia Dec 2025
December 2025
Chromatography Articles- Cutting-edge sample preparation tools help laboratories to stay ahead of the curveMass Spectrometry & Spectroscopy Articles- Unlocking the complexity of metabolomics: Pushi...
View all digital editions
Events
Jan 21 2026 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 28 2026 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 29 2026 New Delhi, India
Feb 07 2026 Boston, MA, USA
Asia Pharma Expo/Asia Lab Expo
Feb 12 2026 Dhaka, Bangladesh