Laboratory products
Learn how ATR can be used to conduct variable depth studies of laminates by altering the thickness of a base layer to study the coating
Jul 07 2021
Introduction
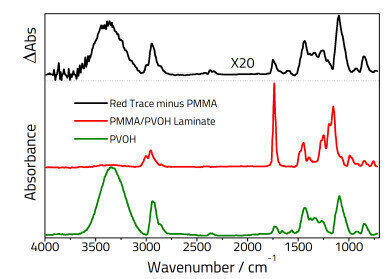
Polymer laminates are commonly employed as coatings in the packaging and lubricant industries. The characterisation of one polymer in the presence of another is important in areas such as adhesion, biocompatibility, and filtration. The ATR technique is known to provide molecular information as a function of depth but it has not been employed extensively to analyse polymer laminates. This application note demonstrates quantitative information can be obtained on polymeric coatings (on a base polymer) using the ‘barrier film’ technique utilising the Specac 25 Reflection Variable Angle ATR accessory.
The 25-Reflection Variable Angle ATR accessory is ideally suited for weakly absorbing samples. Depth of penetration can be tuned by adjustment of the angle of incidence.
• Up to 25 internal reflections (at 45∞ angle of incidence) for highly sensitive ATR analysis
• Tune depth of penetration and peak intensities by varying the angle of incidence from 30∞ to 60∞
• Dedicated crystal holders for solid samples, liquid samples, and pastes
• Choice of crystal materials (KRS-5, ZnSe, Si, and Ge)
Theoretical Background
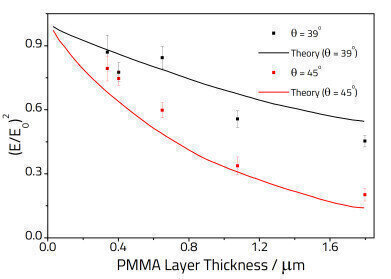
For unpolarised light incident at angle θ on the surface of an ATR crystal the electric field E, at distance z away from the surface is:
E = E0 exp(-z/dp)
Where dp is the penetration depth. It varies by wavelength λ according to the formula:
dp = λ/(2π √(n12 sin2 θ – n22))
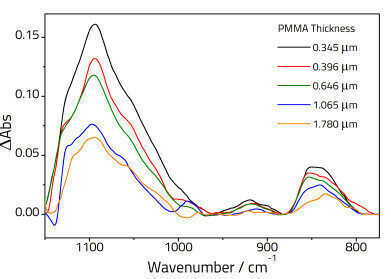
Where n1 and n2 are the refractive indices of the crystal and the polymer respectively. The principle of the barrier film procedure is that for a given θ, n1, and λ the effective penetration of the electric field into the polymer coating depends on the thickness of the base layer. Furthermore, the electric field at the base/coating interface (for a given base polymer thickness) can be varied by altering the incident angle or by changing the ATR crystal (i.e. by changing n1). Infrared intensities depend on the square of the electric field and should therefore show the same dependence as (E/E0)2 when z is varied.
Experimental
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) films of varying thicknesses were deposited onto a zinc selenide ATR crystal (12 reflections) from dichloromethane using the dip coating procedure. A thin layer (0.1 μm) of polyvinyl alcohol (PVOH) was deposited as a coating by the same technique using water as a solvent. At each stage samples were dried in the oven at 60°C. the thickness was determined to ±5% using an α-stepper…
To read more about our Application Notes check out our website.
More information online
Digital Edition
Lab Asia Dec 2025
December 2025
Chromatography Articles- Cutting-edge sample preparation tools help laboratories to stay ahead of the curveMass Spectrometry & Spectroscopy Articles- Unlocking the complexity of metabolomics: Pushi...
View all digital editions
Events
Jan 21 2026 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 28 2026 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 29 2026 New Delhi, India
Feb 07 2026 Boston, MA, USA
Asia Pharma Expo/Asia Lab Expo
Feb 12 2026 Dhaka, Bangladesh