-
 Associate Professor Terry Steele (right) and Dr Ivan Djordjevic (left) holding CaproGlu in a syringe, which is cured by a low dose of UV light after it is applied on a soft tissue surface.
Associate Professor Terry Steele (right) and Dr Ivan Djordjevic (left) holding CaproGlu in a syringe, which is cured by a low dose of UV light after it is applied on a soft tissue surface. -
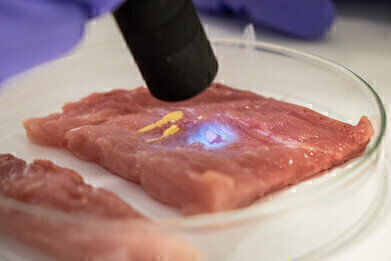 Liquid CaproGlu applied to meat being cured by UV light, turning into biorubber.
Liquid CaproGlu applied to meat being cured by UV light, turning into biorubber. -
 NTU materials scientists Associate Professor Terry Steele (right) and Dr Ivan Djordjevic (left) working in the lab and demonstrating the use of CaproGlu on slices of meat bought from a supermarket.
NTU materials scientists Associate Professor Terry Steele (right) and Dr Ivan Djordjevic (left) working in the lab and demonstrating the use of CaproGlu on slices of meat bought from a supermarket.
News
Singapore Scientists Develop ‘biorubber’ Glue for Faster Surgical Recovery
Sep 08 2020
Materials scientists from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have invented a new type of surgical glue that can help join blood vessels and close wounds faster and may also serve as a platform to deliver pain relief drugs.
In a paper published in Elsevier’s Biomaterials in July jointly with clinicians from Singapore General Hospital (SGH), the NTU researchers showed that their glue can bond soft tissues including muscle and blood vessels, even when their surfaces are wet.
Named CaproGlu, it is activated by a low dose of ultraviolet (UV) light that cures it in seconds, turning it from a liquid glue into a solid but flexible biorubber - a biocompatible material that can be resorbed by the tissue after a few weeks.
The team showed in animal experiments that blood vessels can be rejoined with just four stitches and a mesh wrapper dipped in CaproGlu, compared to the usual eight stitches that are required for a reliable and unobstructed join. The authors estimate that this will reduce surgery time by 25%, as surgeons spend less time and effort stitching up blood vessels and tissues.
More information online
Digital Edition
Lab Asia Dec 2025
December 2025
Chromatography Articles- Cutting-edge sample preparation tools help laboratories to stay ahead of the curveMass Spectrometry & Spectroscopy Articles- Unlocking the complexity of metabolomics: Pushi...
View all digital editions
Events
Jan 21 2026 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 28 2026 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 29 2026 New Delhi, India
Feb 07 2026 Boston, MA, USA
Asia Pharma Expo/Asia Lab Expo
Feb 12 2026 Dhaka, Bangladesh


















