Laboratory products
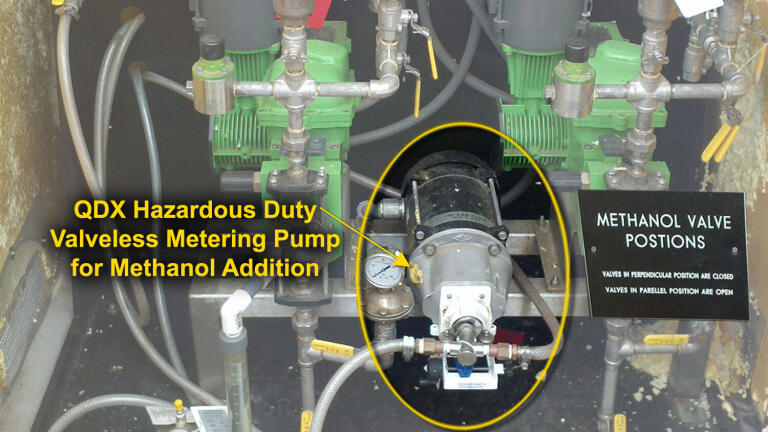
For small and mid-size treatment facilities, Fluid Metering, Inc’s (FMI) valveless QDX metering pump is the answer for low volume addition of methanol for nitrate removal in wastewater effluent.
The release of high nitrogen concentrations of wastewater effluent into bays and watersheds is of great environmental concern as it can have a devastating effect on water ecosystems. Through a process known as ‘denitrification’, water treatment facilities convert the excess nitrate into nitrogen gas, which is then vented into the atmosphere.
The CeramPump® QDX Hazardous Duty Metering Pump from Fluid Metering has proven to be an excellent choice for methanol metering for waste water denitrification due to its unique valveless design. This is especially applicable in small to mid-size treatment facilities where flow rates are extremely low causing valved pump designs to become air-bound and lose prime.
The CeramPump® has only one moving part in contact with the process fluid, a rotating and reciprocating ceramic piston. Similar to conventional piston pumps, the piston’s reciprocation performs the pumping function. However, this is where the similarity to conventional piston pumps ends.
The piston simultaneously rotates during the pumping cycle and is synchronised to alternately open and close the inlet and outlet ports of the pump effectively functioning as a valve. At no point are the inlet and out ports interconnected, thus eliminating the need for check valves. The pump drive is FMI’s QDX Hazardous Duty Drive, typically required for pumping methanol