-
 Red velvet mites accumulate carotenoids from pollen that give them their bright red colour. Credit: Satoshi Shimano from Hosei University and Masahiro Osakabe from Kyoto University
Red velvet mites accumulate carotenoids from pollen that give them their bright red colour. Credit: Satoshi Shimano from Hosei University and Masahiro Osakabe from Kyoto University -
 Red velvet mites accumulate carotenoids from pollen that give them their bright red colour. Credit: Takamasa Memoto
Red velvet mites accumulate carotenoids from pollen that give them their bright red colour. Credit: Takamasa Memoto
News
Scientific Significance of Red Colour in Balaustium Murorum Mites Revealed by Study
Mar 06 2023
Balaustium murorum, or the red velvet mite, lives in harsh conditions among rocks and concrete, enduring intense sunlight and ultraviolet radiation. These non-parasitic mites feed on pollen and hatch from eggs laid during the previous summer. Their bright red coloration, which can spark both fascination and fear due to the association of red with danger, has received little scientific attention. However, a recent study [1] conducted by researchers from Hosei University and Kyoto University in Japan has shed light on the protective function of the mites' striking pigment.
"Every year, the number of online searches related to the red velvet mite shoots up in early spring. Many people consult the internet to know if this mite is harmful and whether its bright red colour signifies that it has sucked blood. But the red velvet mite never acts as a parasite on other organisms,” said Professor Satoshi Shimano from Hosei University. "While we sigh in relief, knowing that these mites are mostly harmless, one does tend to wonder whether the distinct red colour offers a specific survival advantage considering the harsh environments that red velvet mites live in."
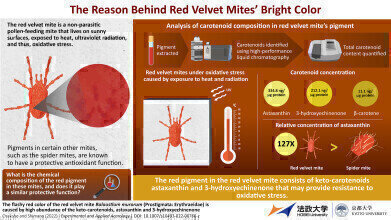
To investigate whether the red velvet mite's bright pigmentation plays a similar protective role, the researchers identified and quantified carotenoids present in the arachnid's body. A chemical-profiling analysis revealed that carotenoids in the red velvet mite were primarily composed of astaxanthin (60%), followed by 3-hydroxyechinenone (38%), both of which are known to be powerful antioxidants.
Professor Masahiro Osakabe from Kyoto University added: “Astaxanthin concentration in the red velvet mite was 127-fold higher than that in spider mite, Panonychus citri, which is an astaxanthin-rich species. This is one of the highest known levels of microarthropods, including crustaceans. Hence, the red velvet mite’s colour is the result of high concentrations of keto-carotenoids, which act as antioxidants against reactive oxygen species that form in harsh environments, due to strong ultraviolet rays and radiant heat.”
Red velvet mites are not vulnerable to predators despite their bright red coloration, as they are only active in early spring before other insects and their natural enemies such as ants and predatory stink bugs do not have photoreceptors for red. This adaptation may also explain why the mites are attracted to hot environments. Hence, their striking red hue is not expected to have a significant impact on their predators' hunting behaviour.
In conclusion, the bright red coloration of the red velvet mite, which is often perceived by humans as a warning signal, has been found to be a benign adaptation that serves a protective function. Rather than signalling danger, the red hue helps the mites stay active in harsh sunlight conditions.
More information online
1. The flashy red color of the red velvet mite Balaustium murorum (Prostigmata: Erythraeidae) is caused by high abundance of the keto-carotenoids, astaxanthin and 3-hydroxyechinenone by Masahiro Osakabe Satoshi Shimano was published in Experimental and Applied Acarology
Digital Edition
Lab Asia Dec 2025
December 2025
Chromatography Articles- Cutting-edge sample preparation tools help laboratories to stay ahead of the curveMass Spectrometry & Spectroscopy Articles- Unlocking the complexity of metabolomics: Pushi...
View all digital editions
Events
Jan 21 2026 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 28 2026 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 29 2026 New Delhi, India
Feb 07 2026 Boston, MA, USA
Asia Pharma Expo/Asia Lab Expo
Feb 12 2026 Dhaka, Bangladesh


















