Growing demand for analytical laboratory services (and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic) will see the industry grow globally to about $492 million by 2027. Batch Release Testing shows the biggest growth in the market, estimated to increase at 9% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR). To keep up with the expected demand over the next seven years, you’ll need to know all the latest techniques and analytical methods that could affect your SPE workflows.
Seventy Years of Analytical SPE Workflows
The past 20 years have seen great developments in laboratories. New sorbent materials and high selective mechanisms such as molecular imprinted polymers, antibodies, antigens, and others increased SPE’s applications and potential.
Due to its versatility and efficiency, including the low environmental impact and reduced volume of solvents required, SPE is the preferred method for sample cleanup and trace enrichment. Large application fields, like contaminant isolation from environmental and food matrices, now depend on modern SPE techniques. Additionally, SPE is also popular in drug extraction workflows from biological fluids in forensic labs and the DMPK disciplines.
Due to its versatility and efficiency, including the low environmental impact and reduced volume of solvents required, SPE is the preferred method for sample cleanup and trace enrichment.
With new formats such as magnetic beads or associated to innovative technologies such as Exclusion based Preparation (ESP), SPE allows efficient clean-up for the isolation of nucleic acids and targeted protein in Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) workflows or to research weakly bound protein complexes not easily accessible by other techniques.
Below we will discuss some of the latest considerations for your SPE processes.
Common Workflow Steps for Solid Phase Extraction
Commonly, there are four steps involved in an SPE method. The intent is to simplify complex sample matrices, purify the analytes of interest, fractionate a complex mixture of active compounds, or concentrate any trace levels of analytes. While different strategies and extraction schemes may apply depending on the exact application of the SPE process, the main steps are:
- Conditioning – This step aims to wet and activate the sorbent to assure good conditions for targeted compound retention
- Loading – Sample materials are loaded on the solid sorbent to retain the analytes of interest.
- Washing – Once you’ve retained the analytes, you wash the sorbent to remove the remaining interferences
- Eluting – The final step is to elute the sample from the sorbent using an elution solvent with a stronger affinity for the target compound than the sorbent

Both the loading and eluting steps aim to ensure the sufficient and reproducible binding (or nonbinding) of interactions. With perfect control of the flow rates used in these processes, it’s easier to produce reliable results in samples.
The historic format uses SPE cartridges and a vacuum manifold, which makes it a labor-intensive process. It requires lab technicians to pay close attention to every step for flow rate fluctuations and cartridges drying during the process.
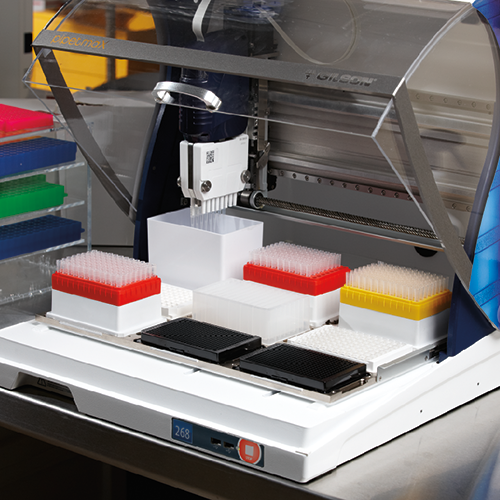
A more efficient method uses a positive pressure approach, with Gilson’s ASPEC® Positive Pressure Manifold (PPM) which helps improve reproducibility and recovery. Suitable for both low and high viscosity solutions, you can combine the ASPEC PPM with SPE Cartridges and 96-well plate formats for forensic, clinical, and food or beverage sampling in your lab.
Automating SPE Workflows
To allow chemists to control the entire process and to increase analytical throughput, Gilson has a family of software options, like TRILUTION® LH, and instruments that support a range of SPE formats and automate the following steps of your workflow
Pretreatment of Samples
In addition to the SPE steps automation, Gilson’s instruments can achieve other manual liquid handling tasks required during pretreatment of samples. It’s possible to automatically add and mix reagents for buffers or homogenization before sample loading. In cases where labs work with high-concentrated samples, technicians can dilute samples during the pretreatment step.
Automating the SPE Steps
With its mobile rack technology and its high flexibility, Gilson’s ASPEC liquid handlers can fully automate your SPE protocols. Modern lab instruments allow for complex workflows such as multi-dimensional SPE that use multiple SPE formats in the same protocol. Automated SPE workflows can reduce tedious manual tasks by efficiently separating analytes by family (i.e. lipids fractionation).
For greater accuracy, sample vessels can be rinsed and the solvent can be loaded. To preserve their integrity, the samples and eluates can be stored in closed vial tanks to the septum-piercing capability.
The TRILUTION LH Software allows automated injection processes that are suitable for SPE techniques that don’t require a solvent exchange or dry-down step for the eluent used. You can automate the transfer of liquids to other vessels, helping streamline the final determination step by placing the samples directly on the analytical instrument.
Benefits of Automating Your SPE Workflow
Sample preparation remains one of the most labor-intensive steps in the analytical method while also being prone to human error. Automating the SPE workflow can increase throughput and the capacity of a lab while reducing the burden on laboratory staff. An automated system will take the same amount of time but can run continuously and free up scientists to focus on other projects or tasks.
With a single probe ASPEC® GX-241 or ASPEC® GX-271 system, you can protect sample integrity and improve data traceability while the four probes ASPEC® GX-274 also increases throughput processing up to 4 times more samples in the same period.
Automate Your SPE Workflow with Gilson SPE Instruments
If you’ve developed an SPE workflow using manual applications, it’s possible to automate these methods easily using our SPE instruments and systems. You can optimize your process for greater consistency, improve your regulatory compliance, and reduce human error.
Developing an automated SPE solution as part of your overall analytical workflow allows you to run your workflows unattended. You can also improve your Electronic Record Management (ERM) processes and generate the necessary log files to validate your methodology using the TRILUTION LH software.
Finally, you’ll benefit from greater consistency in your liquid handling and sampling purification processes with continuous optimization and improvement of the entire SPE workflow.
Gilson Guide to SPE Automation
For some further reading and a complete overview of the SPE instruments and automation capabilities available from Gilson, see this guide.
Read More